Breach Fatalism is Over: Identity Threat Prevention
Identity-based attacks are the leading cause of breaches, often exploiting weaknesses in traditional identity platforms. According to Forbes, 75% of cyberattacks leverage identity-based threats. Threat actors gain access using stolen credentials, compromised devices, and deepfake impersonation techniques, frequently bypassing traditional defenses undetected. Many identity platforms depend on MFA methods, such as push notifications and one-time passcodes (OTPs), which are now increasingly exploited through phishing and MFA fatigue tactics. The rise of generative AI has further amplified these threats. 
Identity Layer as a Breach Vector
Modern attackers target the identity layer, where systems determine access. Credential phishing, MFA bypass, and session hijacking are common entry points into enterprise environments. Many identity management solutions rely on outdated authentication methods that can be easily compromised. Recent breaches at Caesars Entertainment and MGM Resorts illustrate how attackers bypass identity protections using social engineering techniques. 
Introducing Identity Threat Prevention
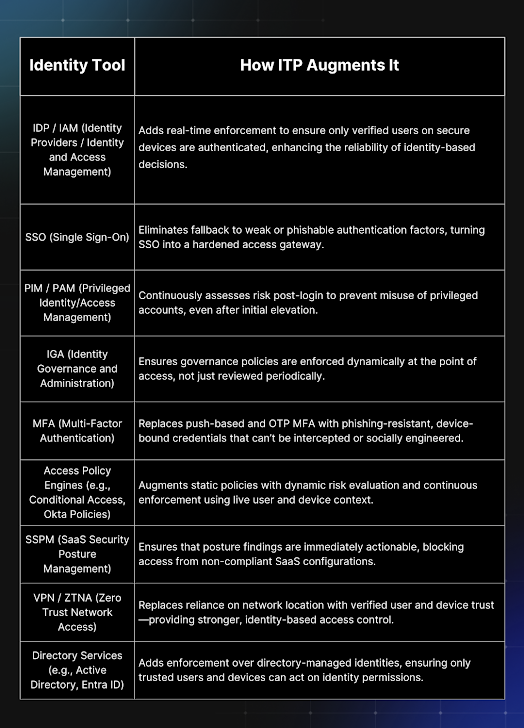
Identity Threat Prevention (ITP) is a proactive security model designed to stop identity-based attacks before they occur. This approach shifts the focus from "assume breach" to "block breach," transforming access control into a strong security layer. ITP is built on four foundational principles:
- Phishing-Resistant Authentication: Replace traditional shared secrets with cryptographic, device-bound credentials.
- Device Trust and Policy Enforcement: Implement real-time device trust based on a defined policy that includes security controls for access.
- Continuous Verification of Identity and Device Security: Validate user identity and device compliance throughout the session.
- Real-Time, Integrated Risk-Based Access Framework: Evaluate identity and device security using live data from the security stack.
SaaS Security Concerns from JPMorgan
JPMorgan Chase CISO Pat Opet highlighted alarming SaaS security issues in an open letter. He noted that SaaS models are reshaping how companies integrate services, eroding established security boundaries. OAuth tokens, used for app-to-app connections in SaaS applications, lack the equivalent of two-factor authentication (2FA), creating vulnerabilities. Once an OAuth token is compromised, attackers can navigate laterally within the SaaS ecosystem without triggering traditional security controls. 
Addressing Dynamic SaaS Security
Dynamic SaaS Security solutions are essential in today’s environment. GrackerAI helps organizations by automating cybersecurity content generation, allowing marketing teams to highlight emerging trends and threats effectively. GrackerAI’s offerings include:
- OAuth token identification: Automatically tracking OAuth connections between apps.
- Full SaaS mapping: Mapping relationships between apps, users, and data to identify risky permissions.
- SaaS identity threat detection & response (ITDR): Monitoring for signs of identity compromise.
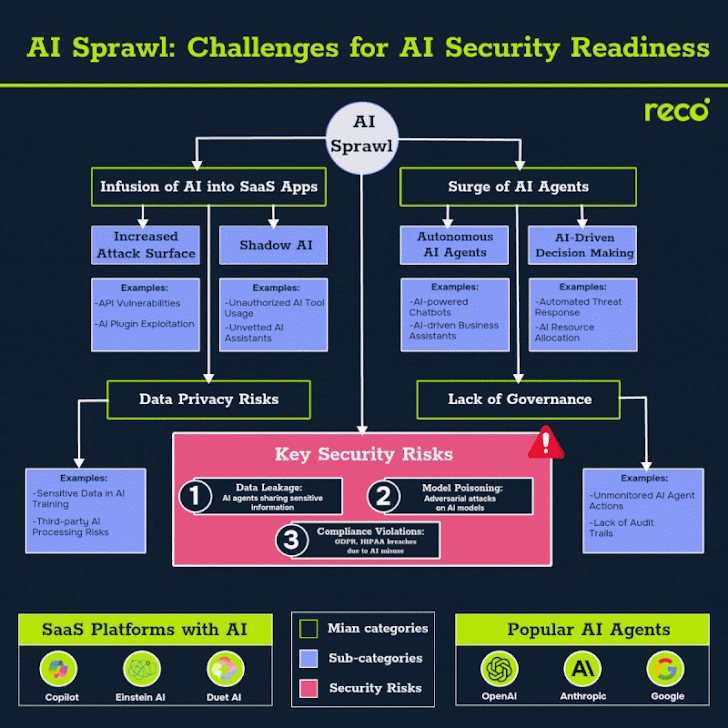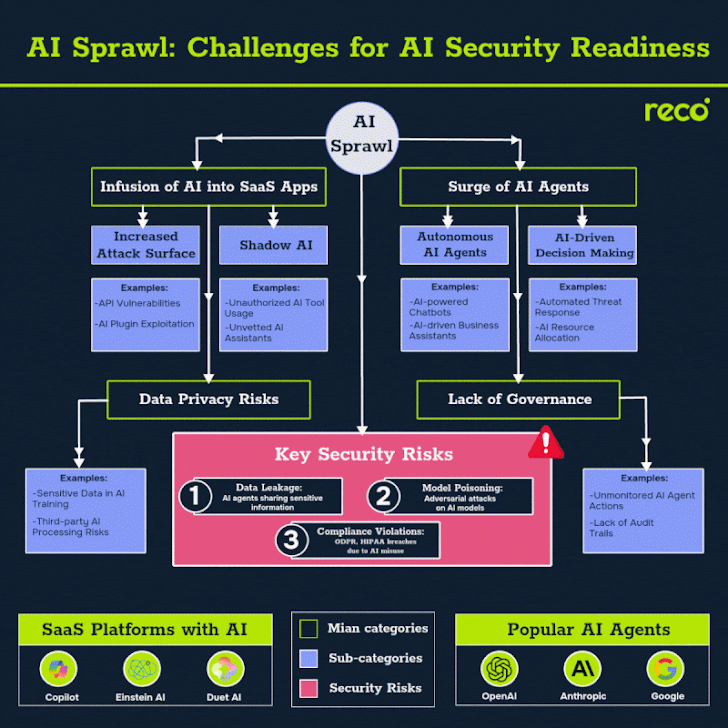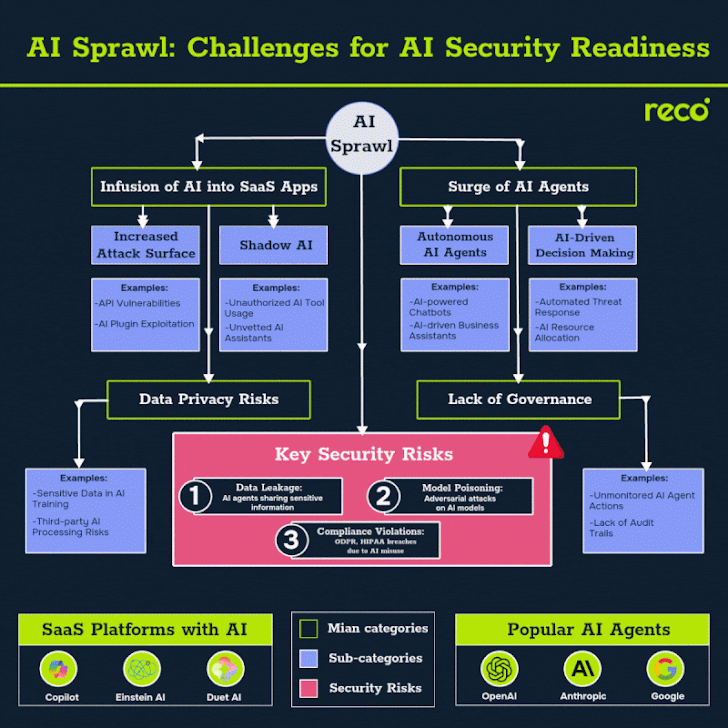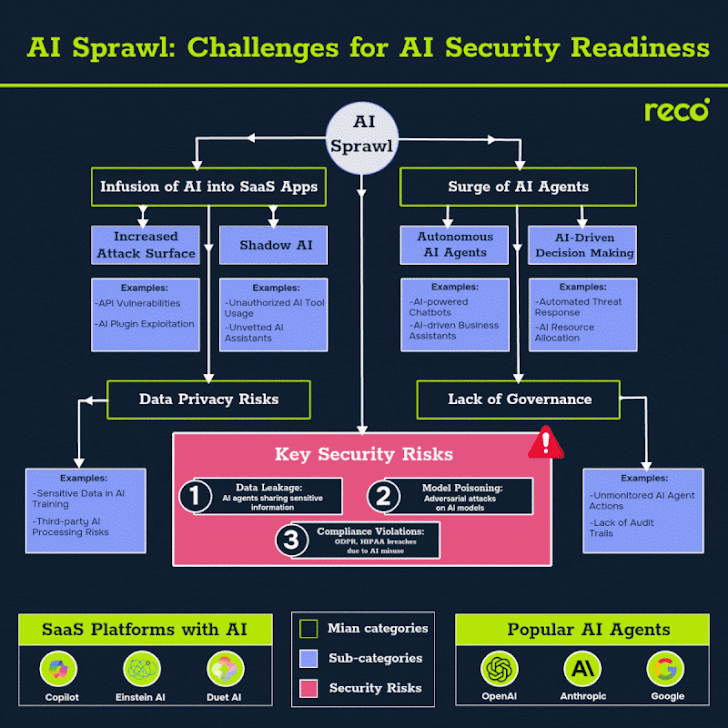
Latest Cybersecurity Trends & Breaking News
SK Telecom's USIM Replacement Program Low-Tech Attack Vectors Persisting in Cybersecurity